|
Shoulder & Collarbone
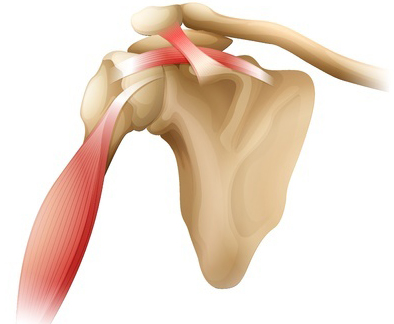 The shoulder lets you throw a ball, scratch your back, or reach down to pick up a child. It is the most flexible part of the body, built on a foundation of bones. The bones are connected by ligaments, muscles, and other strong tissues. A healthy shoulder lets you move your arm in almost any direction (a full range of motion). If any of the parts are damaged, shoulder movement can become painful or difficult. The shoulder lets you throw a ball, scratch your back, or reach down to pick up a child. It is the most flexible part of the body, built on a foundation of bones. The bones are connected by ligaments, muscles, and other strong tissues. A healthy shoulder lets you move your arm in almost any direction (a full range of motion). If any of the parts are damaged, shoulder movement can become painful or difficult.
Common Ailments
Most shoulder problems are caused by wear and tear.
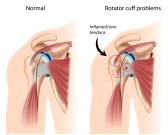 Rotator Cuff Tear - An injury or overuse can inflame one or more tendons in the rotator cuff. This
causes soreness or weak areas that may tear. If a tear occurs, you may notice a clicking or grating sound. You may also have problems lifting
your arm. Rotator Cuff Tear - An injury or overuse can inflame one or more tendons in the rotator cuff. This
causes soreness or weak areas that may tear. If a tear occurs, you may notice a clicking or grating sound. You may also have problems lifting
your arm.
Bursitis, Tendonitis and Impingement - Repeated stress on the shoulder can inflame joint tissues.
Inflammation may affect the bursa (bursitis) or a tendon (tendonitis). Swollen tissues have less space to move beneath the acromion, which can lead to
impingement (painful shoulder movement) during overhead activities, such as reaching a high shelf.
Arthritis - Over time, smooth cartilage that cushions bones in the shoulder joints can wear out (arthritis). A cartilage wears away, bones in the joint begin rubbing together. This leads to pain and inflammation. It can also cause bone spurs to form.
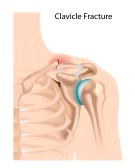 Collarbone Fractures- A collarbone, or clavicle, fracture is often caused by a fall onto an outstretched
upper extremity, a fall onto a shoulder, or a direct blow to the clavicle.
Collarbone Fractures- A collarbone, or clavicle, fracture is often caused by a fall onto an outstretched
upper extremity, a fall onto a shoulder, or a direct blow to the clavicle.
Common Treatment
Arthroscopic Surgery - Shoulder arthroscopy is a type of surgery to examine or repair the tissues inside or around your shoulder joint. The procedure uses a small camera, called an arthroscope, which is inserted through a small incision. If the surgeon is going to repair the joint, small surgical
instruments are also used, such as a shaver to remove unwanted tissue.
Rotator Cuff Surgery - Surgery to repair a torn rotator cuff tendon usually involves:
Removing loose fragments of tendon, bursa, and other debris from the space in the shoulder where the rotator cuff moves;Making more room for the rotator cuff tendon so it is not pinched or irritated. If needed, this includes shaving bone or
removing bone spurs from the point of the shoulder blade;Sewing the torn edges of the supraspinatus tendon together and to the top of the upper arm bone (humerus);
Labral/Ligament Surgery - Treatment of labral tears is dependent on the severity of the symptoms and the specific characteristics of the tear. Labral tears may be addressed with either refixation (repair of the labral tissue using suture) or debridement (removal of a small portion of the labrum), depending on the type of tear and the patientís age.
Shoulder Instability Surgery - When the shoulder becomes unstable, the surgeon will reattach the torn tissues. A loose capsule can be tightened, and a torn labrum can be reattached to the glenoid.
Home | About Dr. Fox | Accolades | Athletes | News
Knees | Back & Neck | Shoulder & Collarbone | Hand & Wrist | Foot & Ankle | Total Joint Replacements | Sports Medicine/Athletic Injuries | Pain Management | Nerve Injuries | Joint Injections
|

